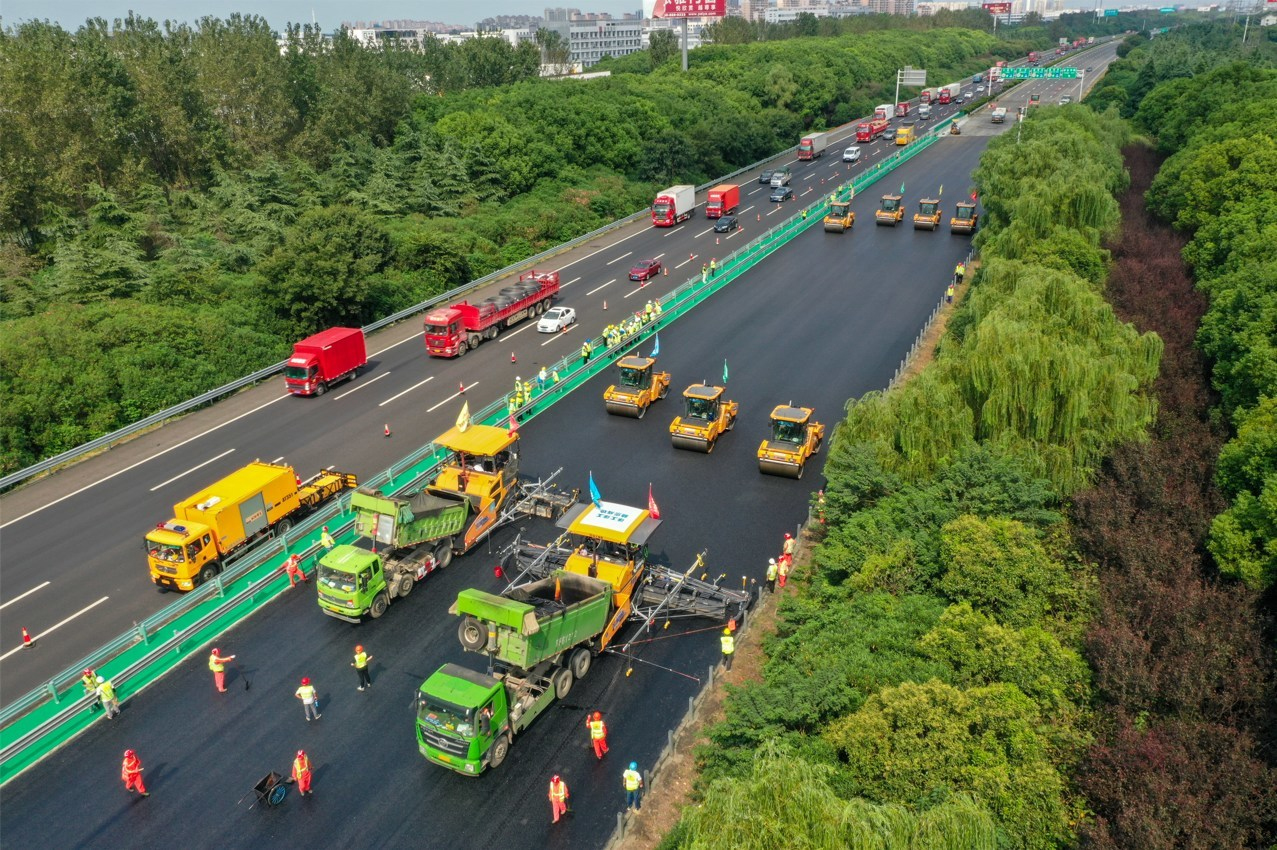
Chinese construction equipment maker the Xuzhou Construction Machinery Group (XCMG) has used a fleet of autonomous road construction vehicles to resurface a stretch of China’s busiest motorway, the Nanjing-Shanghai Expressway.
According to XCMG, the use of the vehicles is a “landmark event” in the development of smart road maintenance.
The units used on the refurbishment of the Suzhou Road segment of the highway included 10 tandem road-rollers and two large-width pavers, all of which were controlled and coordinated by a Baidu satellite positioning station. Other smart systems used on the project included inertial navigation and obstacle recognition.
Li Xin, assistant general manager of Jiangsu Xiandai Road & Bridge, the contractor in the charge of the work, commented in a press statement: “This unmanned road maintenance and construction project allowed us to reach the ‘intelligent maintenance’ stage.
“The inspection pass rate is much higher than that of traditional manual construction, and XCMG’s unmanned technologies have excelled in construction efficiency and control accuracy.”
Among the advantages claimed for robot road work is the even application of asphalt. This is controlled by radar, and can lay a 120mm pavement with an accuracy of plus or minus 1mm.
The press statement added that the unmanned fleet met “all construction and maintenance requirements through the grid format tests of thickness, compaction and friction coefficient”.
The Suzhou Road project followed smaller-scale demonstrations on other Chinese road schemes, such as the Liuzhou-Nanning Expressway, the Beijing-Xiong’an Expressway and the Beijing-Dezhou Expressway.
Lige Xue, a research and development engineer with XCMG, said the company would work to standardise the “highly complex and difficult” business of autonomous construction. He said: “With intelligent sensing and control, digital construction and unmanned technology as the core, XCMG is dedicated to providing customised, high-quality intelligent solutions for customers.”
Further reading: